Low Cost Hydrogen Production
Extreme Temperature
Thermal Reforming Source
Link to Full Document
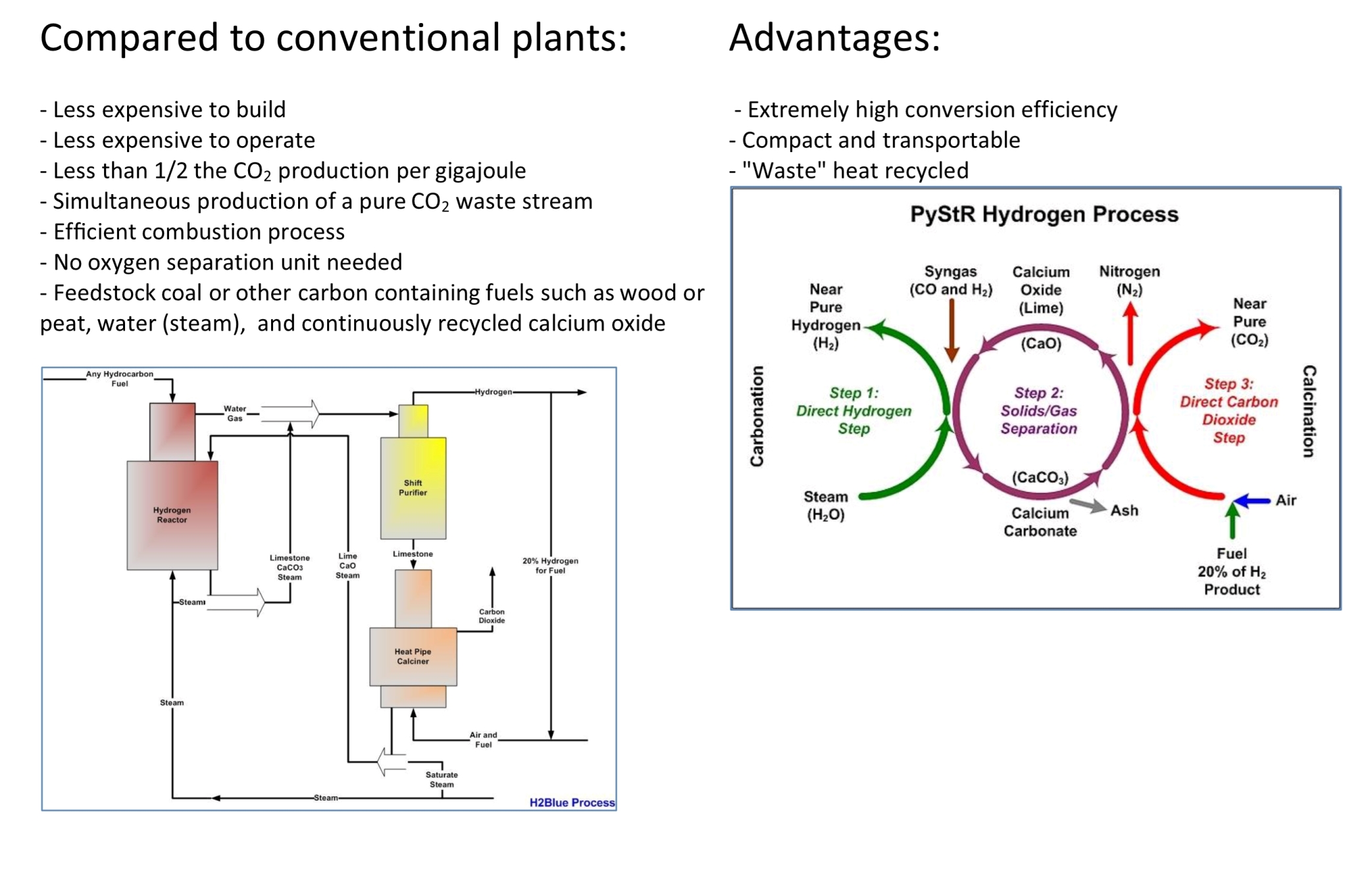
Reactions between carbon (C), water (H2O), Calcium Oxide (CaO), and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) can take place in a single reactor.
Two chemical loops are included in this process. The first chemical loop is the water cycle. Water reacts with organic material to produce H2 and CO2. The Hydrogen produced reacts with O2 in the air and forms water (H2O) and energy.
The second is the calcium cycle. CaO absorbs CO2 in the same reactor where water and carbon react and releases heat during the formation of CaCO3. This heat, however, is released in the reactor and used in the water carbon reaction as mentioned above. As the calcination reaction is an endothermic reaction, heat is absorbed during the regeneration of CaCO3 to CaO. This heat, however, is released in the reactor and used in the water carbon reaction as mentioned above. This means the process converts heat energy to chemical energy. For a complete process, raw materials supplied are hydrocarbon, water, and oxygen; products produced are hydrogen, heat, and pure CO2.
This is an efficient energy conversion process.